Introduction
If you’ve never heard of canaliculi, don’t worry—you’re not alone! These tiny structures may be small, but they play a big role inside your body. Found mostly in bones and certain organs like the liver, canaliculi help cells stay connected and share important materials.
Think of canaliculi as tiny passageways or tunnels. They’re like little roads that travel between cells, helping them talk to each other and move nutrients or waste. Without canaliculi, cells wouldn’t be able to work together properly—and your body wouldn’t run smoothly.
In this article, we’ll take a fun and easy look at what canaliculi are, where they’re found, and why they matter. We’ll explain how they affect your bones and other body systems. Whether you’re curious about biology, studying for class, or just enjoy learning how your body works, this guide on canaliculi was made for you.
Let’s begin exploring these microscopic heroes that keep everything moving and connected inside us.
What Exactly Are Canaliculi?
Canaliculi (pronounced “can-uh-LICK-you-lye”) are tiny tube-like structures inside the body. The word comes from Latin and means “small channels,” which is exactly what they are. You can think of them as super thin tunnels that go from one cell to another.
They are most commonly found in bone tissue, helping bone cells communicate. Bone isn’t just a hard, solid block—it’s actually alive and full of cells. These cells need a way to share information and send nutrients. Canaliculi act like message highways and delivery routes rolled into one.
You’ll also find canaliculi in other organs like the liver, where they help with bile movement. In simpler words, canaliculi are like the body’s traffic system, helping things move along in the right direction.
Even though they are super tiny and require a microscope to see, canaliculi are essential parts of how our bodies work every single day.
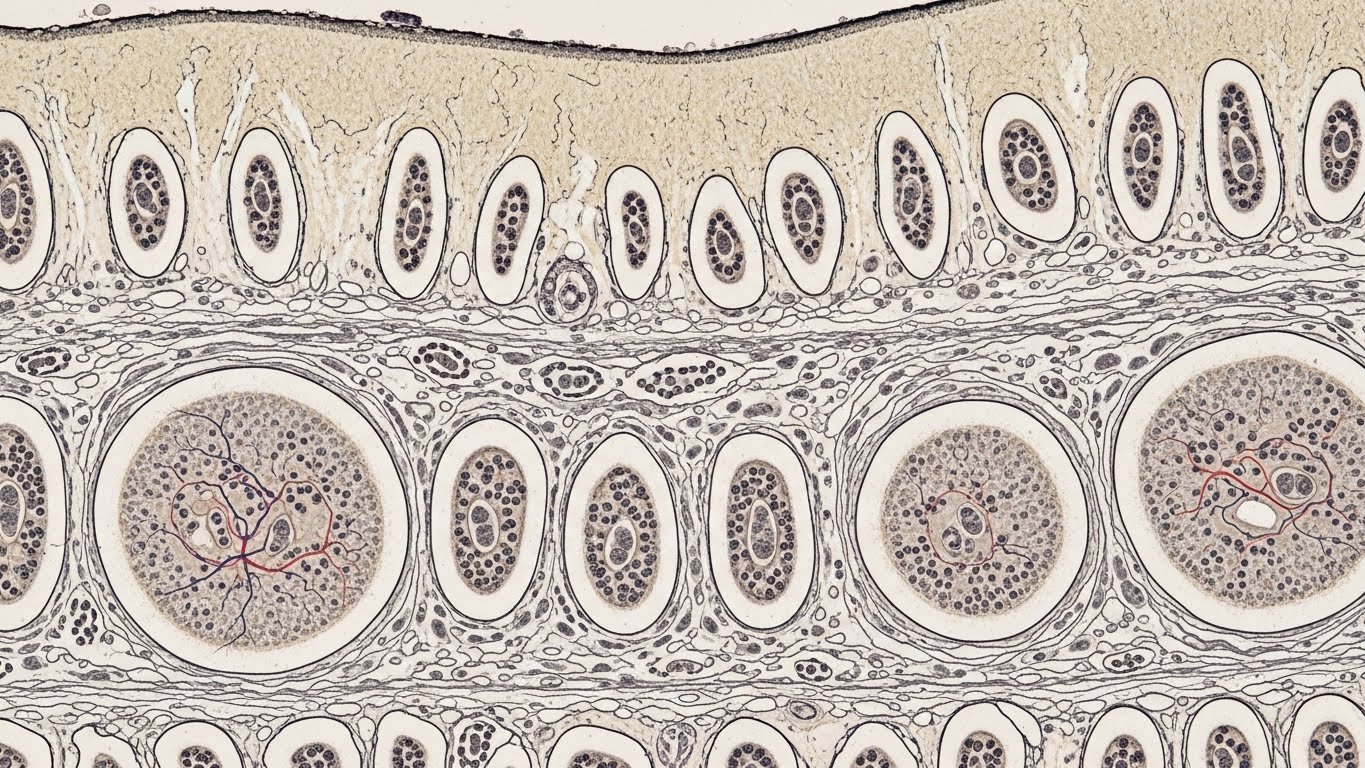
Canaliculi in Bones: Keeping Bone Cells Connected
In the human body, bones are more than just support structures—they are alive, busy, and full of cells working together. In bone tissue, canaliculi are helpful little pathways linking osteocytes, or bone cells, that live inside small spaces called lacunae.
Each osteocyte has little arms, called cell processes, that stretch out and connect through the canaliculi. This allows the cells to talk and share nutrients, even though they are trapped in the middle of a hard bone.
If a bone gets cracked or weak, the osteocytes send signals through the canaliculi to help fix it. Amazing, right?
Without canaliculi, bone cells would be isolated and unable to stay healthy. They would not receive the food, oxygen, or signals they need to do their jobs. So even though these channels are tiny, they’re a huge part of your body’s bone health and repair system.
Canaliculi in the Liver: Helping Bile Flow Smoothly
Besides bones, another place where canaliculi are super important is in the liver. In the liver, they are called bile canaliculi. These microscopic tubes help collect and carry a fluid called bile, which is made by the liver.
The liver’s job includes breaking down fats and getting rid of waste. Bile plays a big part in this process. But to get bile from liver cells to the main bile ducts, it has to travel through these small passageways. And that’s where canaliculi come in.
Just like in bones, these canaliculi act like roads—but this time they’re transporting liquid instead of messages. The bile goes from the liver cells, through the bile canaliculi, and then to larger ducts where it can be stored in the gallbladder or sent into the intestines to help digestion.
Canaliculi in the liver may not be visible, but their job is huge when it comes to digesting your food properly and keeping your body clean from waste.
Why Are Canaliculi So Small?
You might be wondering—why are canaliculi so tiny? Isn’t it harder for stuff to move through small spaces? Actually, their small size is what makes them perfect for their job!
In places like bone tissue, canaliculi have to fit between dense layers of minerals. They need to weave all through the solid structure, connecting cells without weakening the bone itself. Small is smart!
In the liver, thin canaliculi allow bile to pass quietly and safely between tightly packed liver cells before joining larger ducts.
Think of a big city with both highways and narrow alleyways. Sometimes, those small streets are the fastest way from one place to another. Canaliculi are like those hidden, smart shortcuts inside your body.
Even though they’re microscopic, canaliculi have a huge impact due to their size, shape, and clever placement in tissues.
The Science Behind How Canaliculi Work
Canaliculi do more than just look like tiny tunnels—they are fully functional routes where important things are constantly moving.
In bones, these channels let mineral nutrients, oxygen, and waste products pass from the blood supply to cells inside the bone—and back again. It’s like a delivery and trash pickup service working 24/7. The movement happens thanks to fluid traveling through the canaliculi.
In the liver, bile canaliculi help flow bile acids, salts, and waste made by liver cells. These travel from small canaliculi into larger bile ducts and eventually help digest fats in your intestine.
Also, in bone canaliculi, cells send chemical signals to one another. This tells other bone cells when to build or break down areas of the bone tissue.
So, even though canaliculi are super small, they’re extremely active!
What Happens If Canaliculi Get Blocked or Damaged?
Just like roads can get blocked by traffic, canaliculi can also have problems. But when they do, it’s more serious than just a slowdown.
In bone, if canaliculi get damaged—like from a disease or injury—bone cells can’t talk or get nutrients. This may cause them to die, which weakens the bone itself. That can lead to fractures or poor bone healing.
In the liver, blocked bile canaliculi can cause a condition called cholestasis, where bile can’t flow properly. This leads to a buildup of waste, pain, and even yellowing of the skin (jaundice).
So, canaliculi may be tiny, but when things go wrong, the problems can become big very fast.
Doctors sometimes use scans and blood tests to check if something’s wrong. That way, they can work to protect or support damaged canaliculi and prevent bigger issues.
Can You See Canaliculi Without a Microscope?
No—you can’t see canaliculi with your eyes alone. They’re far too tiny.
To view them, scientists and doctors use powerful microscopes, including light microscopes and even electron microscopes for super detailed views. In bone, canaliculi look like branch-shaped lines radiating outward from lacunae (where the bone cells live). In the liver, bile canaliculi look like tiny channels running between liver cells, often with bright stains that highlight them.
Even though we can’t see them without help, their existence is well known and has been studied for a long time. Modern imaging techniques have made studying canaliculi much easier and more accurate, which helps scientists understand diseases that affect bones and the liver.
So even if you can’t spot one with your eye, just know that they’re always working hard behind the scenes to keep your body running strong.
How Canaliculi Help with Communication Between Cells
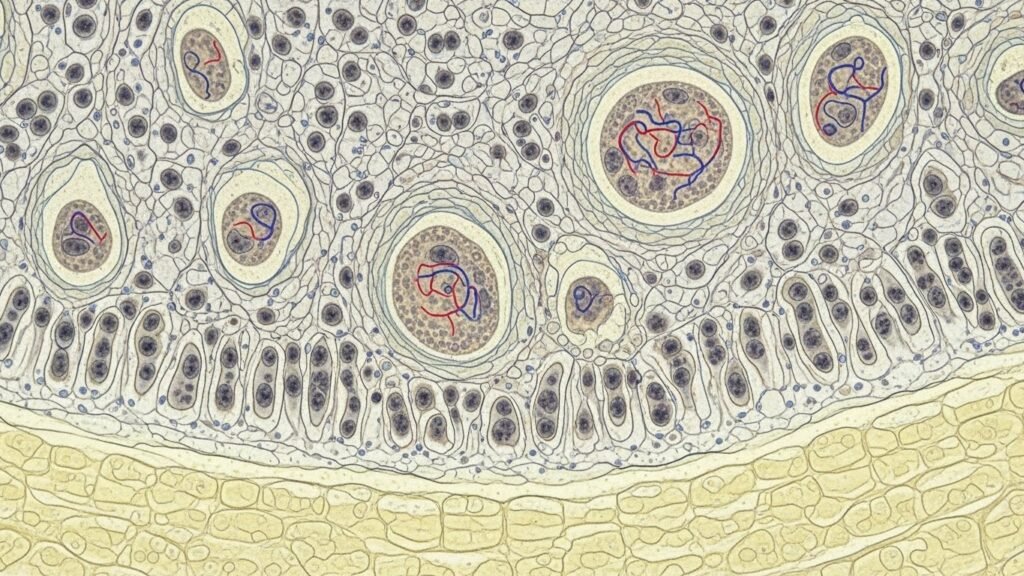
One of the coolest facts about canaliculi is how they help cells stay in contact — even when surrounded by hard material like bone.
In bone, canaliculi let osteocytes send messages back and forth using tiny chemical signals. These signals travel through the fluid inside the canaliculi, kind of like notes passed between friends. When cells say “we need more nutrients” or “there’s damage here,” it creates a team effort to stay strong and healthy.
In the liver, liver cells also communicate through the bile canaliculi system. They coordinate how much bile to produce and when. That helps digestion work like a smooth machine.
In both places, canaliculi are vital talk tracks, making sure everyone is in tune. Without them, our body’s inner teamwork would break down.
It’s these behind-the-scenes connections that keep your body functioning every minute of the day.
Canaliculi and Bone Health as You Age
As you get older, your bones become less dense, and your ability to repair damage slows down. One reason might be related to canaliculi.
Over time, the number and quality of canaliculi may decrease. When this happens:
- Bone cells can’t communicate as clearly.
- Nutrient delivery slows down.
- Waste isn’t cleared away as well.
All these small changes can make bones weaker and more brittle, increasing your risk of being hurt during falls.
That’s why good nutrition (especially calcium and Vitamin D), regular activity, and avoiding smoking are important. They help keep your canaliculi working well so your bones can keep doing their job—even as you age.
Doctors and researchers are working hard to better understand canaliculi’s role in aging bones to find ways to keep us healthier, longer.
Fun Facts About Canaliculi
Here are some cool things you might not know about canaliculi:
- There can be millions of canaliculi in one small piece of bone!
- Canaliculi help bones know where to grow thicker or thinner. They’re like smart messengers.
- The length of all canaliculi in one person could stretch dozens of meters if laid end to end.
- Bile canaliculi also help reduce toxins in the body by helping the liver do its job better.
- Some new research shows canaliculi might also play a role in bone diseases, which could lead to better treatments one day.
You might never see a canaliculus in real life—but now you know how vital they are every day inside you!
FAQs
1. What are canaliculi made of?
Canaliculi are tiny tubes or channels made from cellular extensions and are surrounded by bone or liver tissue.
2. Can canaliculi heal if damaged?
Some canaliculi systems may repair over time, especially in young, healthy people. But severe damage may need medical help.
3. Are canaliculi found all over the body?
Not everywhere. They’re mostly found in bones and the liver, where they’re part of key systems.
4. Do canaliculi carry blood?
No, canaliculi carry nutrients, signals, and fluids—not full blood—but they connect to areas near blood vessels.
5. Are canaliculi the same in bones and liver?
They work similarly, but in bones they connect cells, and in the liver, they help move bile.
6. How do doctors study canaliculi?
By using microscopes, special dyes, and new imaging tools to see how they work and respond to disease.
Conclusion
Even though they’re almost invisible, canaliculi play a massive role in your health. They help keep bones strong, coordinate repairs, and make sure liver functions flow just right. Without them, cells in hard or crowded places would struggle to survive.
From helping bone cells chat, to carrying bile fluid in the liver, canaliculi are always quietly at work. Now that you’ve learned more, maybe you’ll think of them as the tiny heroes doing big jobs.
So, the next time you move, eat, or heal from a bump, thank your canaliculi! They may be small, but they keep your body strong, smart, and working like a team.