
Introduction
Computers have transformed the way we work, communicate, and engage with the outside world, becoming an essential part of our daily life. Each generation of computers has seen a substantial breakthrough in technology and computing power, which has been a remarkable development in the history of computing. This article will take you on a tour through the eras of computers and their impact on society and industry, from the enormous ENIAC to the revolutionary quantum computing.
Different generation of computers :
| Generation Of Computers | Time Period | Hardware Evolution |
|---|---|---|
| First generation | 1940 – 1956 | Vacuum Tube based |
| Second generation | 1956 – 1963 | Transistor based |
| Third generation | 1964 – 1971 | Integrated Circuit (IC) based |
| Fourth generation | 1971 – 1980 | Microprocessor based |
| Fifth generation | 1980 – Present | AI and Quantum computing |
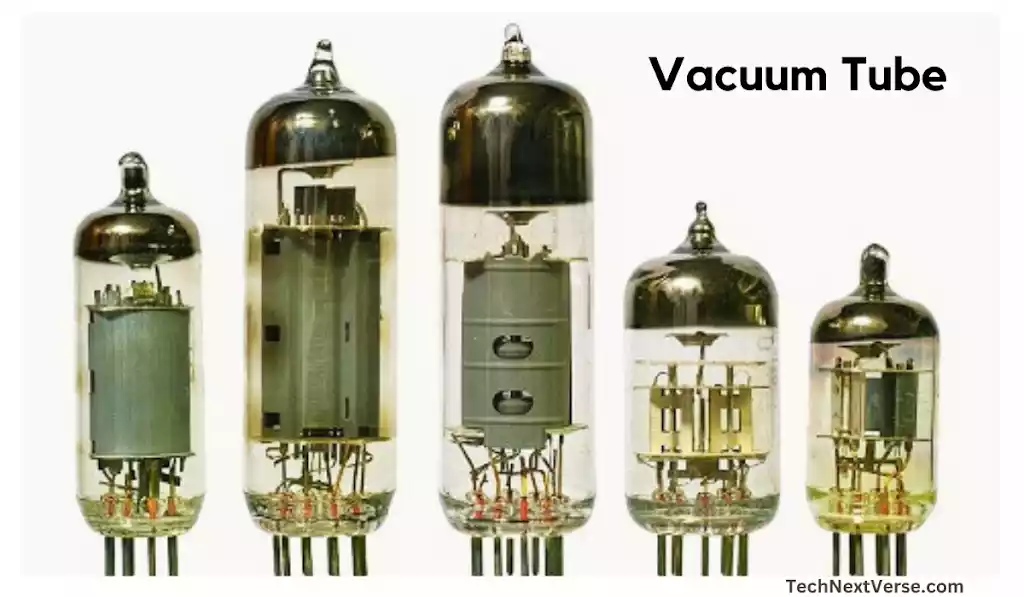
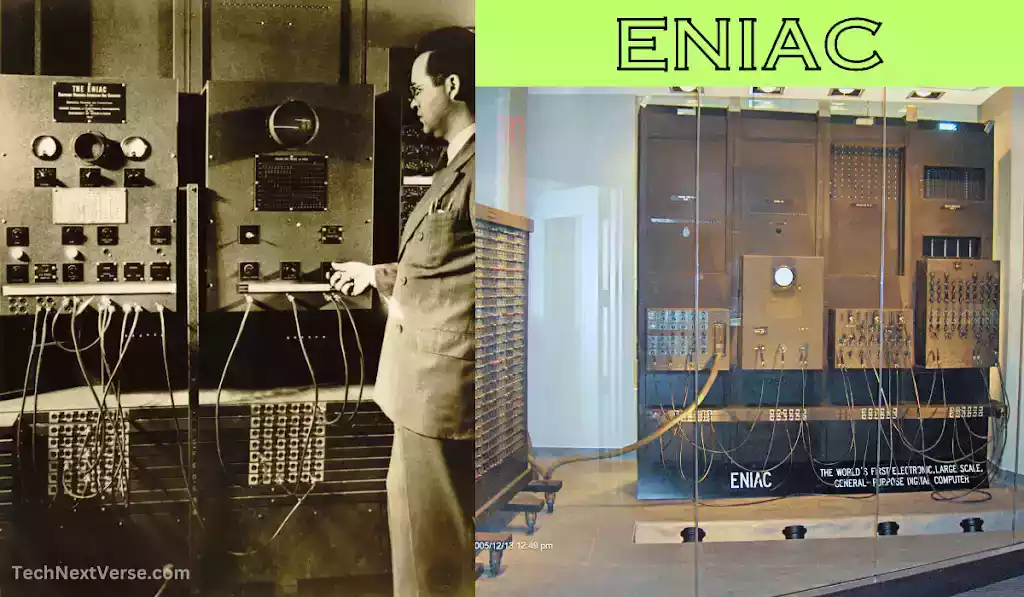
First Generation: ENIAC and the Birth of Computing (1940-1956)
The creation of ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) throughout the 1940s helped define the first generation of computer. ENIAC was a huge computer, made with many vacuum tubes (more than 20,000 vacuum tubes) that took up a full room and was mostly utilized for difficult computations in science and the military. It processed data using vacuum tubes, which made it sluggish and prone to frequent errors.
👉 The first generation’s key characteristics are :
- Vacuum tube technology based.
- Generated a lot of heat.
- Consumed a lot of electricity.
- very Slow performance.
- Taking a lot of space to build it.
- very costly to build.
- Maintenance problem.
- Memory storing devices as magnetic tape.
- non – portable
- machine language as programming language
▨ In this generation, a few of the machines were :
- ENIAC
- IBM 701
- Manchester Mark 1
- UNIVAC
- EDSAC (Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator)
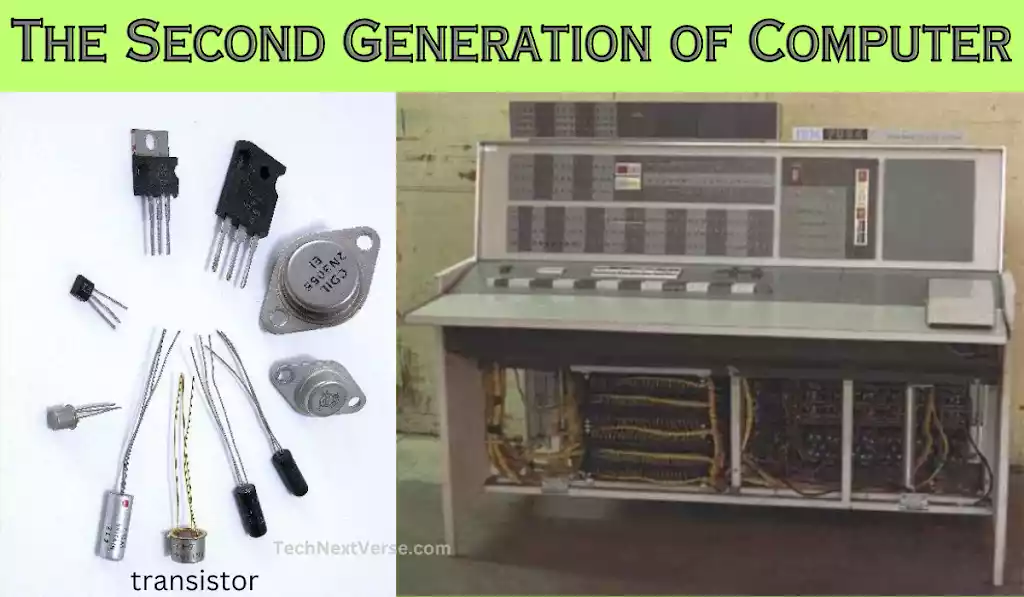
Second Generation: Transistors and the Rise of Mainframes (1956-1963)
With the invention of transistors in the late 1950s, the second generation of computer was born. Computers are now more dependable, effective, and small since these solid-state components have replaced the large vacuum tubes. During this time, mainframe computers gained popularity for use in data processing and commercial applications by big businesses and government agencies.
👉 The second generation’s key characteristics are :
- Transistor based
- Smaller in size than first generation
- Generate less heat than first generation
- faster performance than vacuum tube
- Support machine & assembly languages
- Cheaper to build than vacuum tube
- Consumed lesser electricity than previous
- memory storing device as magnetic tape & disk
▨ Some of the machines in this generation were :
- IBM 7070
- CDC 1604
- CDC 3600
- UNIVAC 1108
- RCA 501
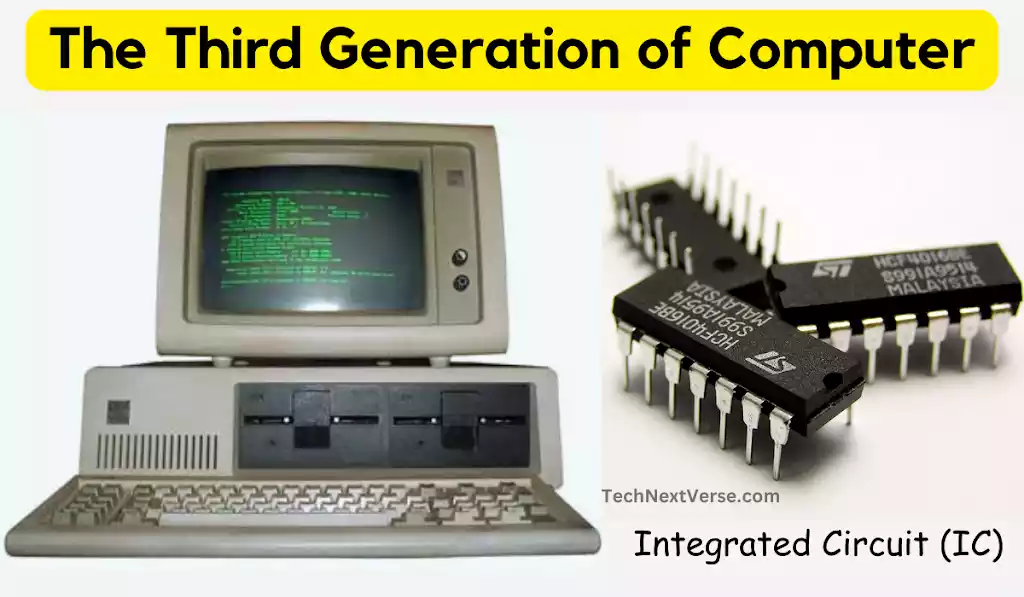
Third Generation: Integrated Circuits and Minicomputers (1964-1971)
The third generation of computers began with the introduction of integrated circuits in the 1960s. (Jack Kilby was the inventor of the IC ). Multiple transistors could be combined on a single chip thanks to integrated circuits, which further reduced the size of computers and increased their processing capacity. Targeting small- to medium-sized enterprises and research institutes, minicomputers were introduced.
👉 The third generation’s key characteristics are :
- IC (integrated circuit) based
- Smaller in size
- Generate less heat than previous
- Faster performance than previous
- Consumed lesser electricity
- Cheaper to build than second generation
- Lesser maintenance
- Magnetic disk for storing device
- Support high-level languages ( FORTRAN-II to IV, BASIC, ALGOL-68, COBOL)
- keyboard, printer, magnetic tape, monitor as input-output device
▨ Several of the machines in this generation were :
- IBM-360 series
- Honeywell-6000 series
- IBM-370/168
- TDC-316
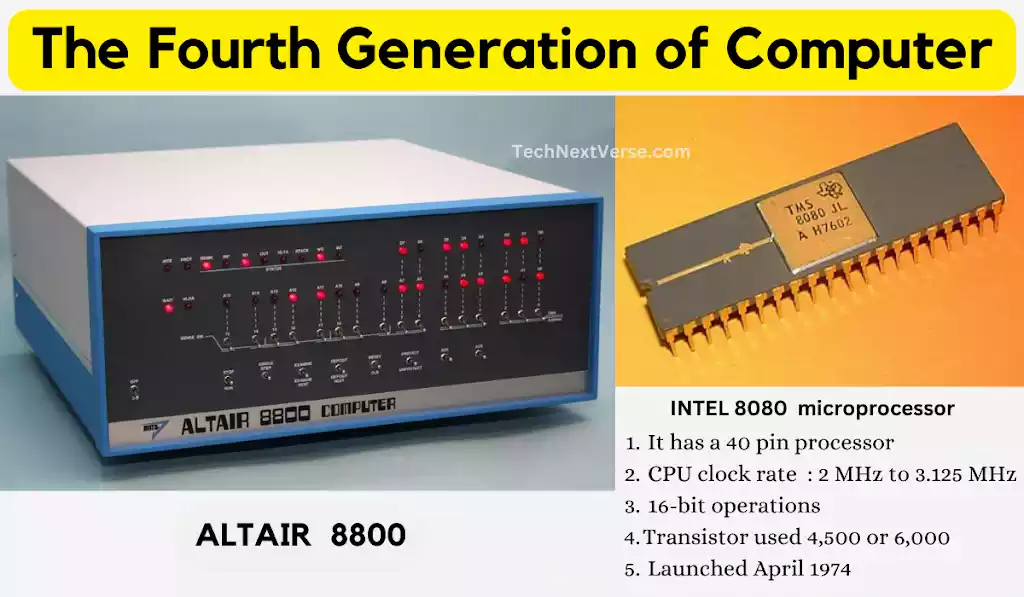
Fourth Generation: Microprocessors and Personal Computers (1971-1980)
With the development of microprocessors in the middle of the 1970s, the fourth generation of computer was born. The computing industry was revolutionized by microprocessors, which placed the whole central processing unit (CPU) on a single chip. Personal computers (PCs), such the Apple II and IBM PC, were created as a result, bringing computing power into people’s homes and workplaces all over the world.
One of the first commercially successful microcomputers was the Altair 8800, which was introduced in 1975 by MITs and it was based on INTEL 8080 microprocessor. It triggered a surge in interest in personal computing and set the stage for later developments that would enable the widespread use of computers in homes.
👉 The fourth generation’s key characteristics are :
- VLSI (very large scale integration) technology based
- Very small in size
- Portable and reliable
- Consumed lesser electricity
- Support internet
- RAM & ROM support for storing devices
- Pipeline processing introduced
- Very much faster than previous generations
- Computers are now widely available.
- Very much cheap
- High level languages(C, C++, Python, C#) are used
▨ Many of the devices in this generation included :
- ALTAIR 8800
- DEC 10
- IBM-5100
- STAR 1000
- Apple Ⅱ
Fifth Generation: Artificial Intelligence and Supercomputers (1980 – Present)
The development of artificial intelligence (AI) and supercomputers defined the fifth generation of computer, which appeared in the 1980s. Expert systems and natural language processing are two examples of AI technologies that have created new opportunities for automation and problem-solving.
Supercomputers became the highlight of this generation, delivering unprecedented processing power and enabling complex simulations and calculations. Their applications ranged from weather forecasting to scientific research.
The Summit supercomputer was as of November 2018 the fastest supercomputer in the world.
🤖 Some well known examples of AI :
- IBM’s Watson,
- Google’s Search engine
- Apple’s Siri,
- Microsoft’s Cortana on Windows 8 to 11,
- OpenAI’s ChatGPT,
- Google’s Bard
👉 The fifth generation’s key characteristics are :
- ULSI (Ultra large Scale Integration) technology based
- Very much small in size
- Portable and reliable
- Artificial intelligence (AI) develops
- Parallel processing introduced
- Very much cheap
- UI becomes more user friendly
- Too much powerful, speed and compact
- Gaming and robotics facilities
- Huge storage capacity & portable
- Development of Natural language processing
▨ Among the devices in this generation were :
- Desktop
- Laptop
- NoteBook
- Play Console
- Super Computer

Sixth Generation: Quantum Computing and Beyond (Future)
The sixth generation of computers is the one we are in right now, and quantum computing is what sets it apart. The principles of quantum physics are used in quantum computing to process data in completely new ways. Quantum computers employ quantum bits, or qubits, which may exist in several states concurrently, as opposed to classical computers, which use bits. This makes quantum computers capable of carrying out intricate computations at extraordinary rates, making them
promise for resolving issues that are at now insoluble.
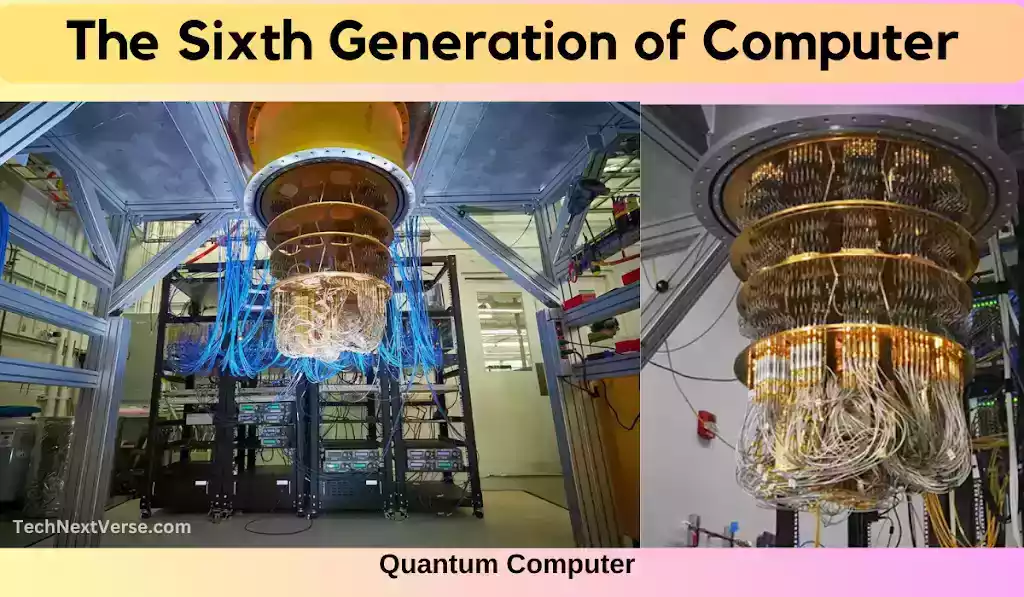
Quantum Computing: The Breakthrough Technology
Quantum computing operates on the principle of superposition and entanglement, where qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously. This ability to handle vast amounts of data simultaneously gives quantum computers their edge over classical ones.
Companies like IBM, Google, and D-Wave have made significant strides in quantum computing research and development. Google’s quantum supremacy experiment demonstrated the ability of a quantum computer to solve a problem faster than any supercomputer.
Read Also :
Challenges and Limitations of Quantum Computing
While quantum computing has a lot of potential, there are also many obstacles to overcome. Because they are so sensitive to environmental disturbance, quantum computers operate best in a stable environment with very low temperatures. Additionally, hard challenges that academics are now working on include resolving error rates and creating algorithms for quantum computers.

Impact of Generations on Society and Industry
The society and industry have been significantly impacted by each generation of computer. Early computers aided in accelerating military development, space exploration, and scientific inquiry. As computers became more widely available, they changed the way businesses operated, resulting in higher levels of productivity and automation across a range of industries.
Evolution of Computer Programming Languages
Computer programming languages also developed with each generation to support the hardware’s increasing capabilities. Developers have benefited from increasingly effective tools as they have progressed from the first machine code instructions to high-level programming languages like C, C++, C#, Python and Java to build complex software programs.
Conclusion
It has been amazing to watch computers evolve from the ENIAC to quantum computing. The world in which we now live has been shaped by successive generations building on the successes of earlier ones. The limits of computers will be pushed even further as technology develops, providing fresh perspectives and possibilities for next generations.
Frequently asked question(FAQs) :
1. What are the generation of computers ?
Ans : Here the generation of Computers below :
- First generation (1940 – 1956) : Vacuum Tube based
- Second generation (1956 – 1963) : Transistor based
- Third generation (1964 – 1971) : Integrated Circuit based
- Fourth generation (1971 – 1980) : Microprocessor based
- Fifth generation(1980 – Present) : Ai and Quantum computing
2. Who invented first generation computer ?
Ans : The first generation of computers were produced between 1946 and 1959. The original electronic calculator, often known as ENIAC—an acronym for “Electronic Numeric Integrated And Calculator”—was created by J.P. Eckert and J.W. Mauchy.
3. Can quantum computers completely replace classical computers ?
Ans : No, quantum computers will not replace classical computers entirely. Quantum computers excel in solving specific types of problems, while classical computers remain more practical for everyday tasks.
4. Are quantum computers commercially available ?
Ans : Yes, some companies (Google, IBM) offer cloud-based access to quantum
computers, allowing researchers and developers to experiment with quantum algorithms and applications.
5. What are the practical applications of quantum computing ?
Ans : Quantum computing’s practical applications include cryptography, drug discovery, optimization problems, artificial intelligence, and climate modeling, among others.
6. What’s the machine language ?
Ans : The fundamental language of computers is machine code, which is often
referred to as machine language. It is made of digital binary integers, is read by the central processing unit (CPU) of the computer, and appears to be a very lengthy string of zeros and ones.
7. Who is Known as the Father of Computers ?
Ans : The father of computers is regarded as Charles Babbage. He was an English
mathematician and inventor. He is recognized as being the inventor of the first automated digital computer. The original Analytical Engine’s blueprints were also created by Charles Babbage in the middle of the 1830s.








Such a good information 🤝👌