Is your computer feeling a bit tired and slow, like it needs a boost? Well, it might be time for an upgrade, and the big question is: “SSD vs HDD which is better?“, why should you go for a trusty but slow Hard Disk Drive (HDD) or a speedy Solid State Drive (SSD)?
In the world of computer storage, two main options dominate – solid-state drives (SSDs) and hard disk drives (HDDs). But what is the difference between HDD and SSD storage, and which one is better for common uses like laptops or gaming?
I’ve been using hard disk and SSD drives for the past few years. So I’ll cover what I face in this article.
Here, I will explain the key difference between SSD and HDD in points and which should you buy.
What is a Solid State Drive (SSD)?

SSDs are a newer form of high-speed storage that stores data on flash memory chips rather than magnetic platters like in traditional hard drives. Some key SSD features:
- Faster speed – SSDs can access data much more quickly, resulting in faster bootup and program loading times. High-end models perform up to 4-5 times faster than HDDs.
- More durable – With no moving parts, SSDs are less likely to break due to damage or drops.
- Quieter operation – SSDs run silently with no disk spin noise.
- Lower power use – SSDs consume less energy, which helps improve laptop battery life.
But SSDs also have downsides like lower capacities and higher costs compared to HDDs of the same size.
SSD Pros:
- Faster speeds (2X to 10X)
- More durable and shock-resistant
- Cool, quiet operation
- Lower power consumption
- Typically more reliable
SSD Cons:
- Lower maximum capacities
- More expensive per gigabyte
Top SSD manufacturers like Western Digital, Crucial, Gigabyte, Samsung etc. are available in the market.
What is a Hard Disk Drive (HDD)?

HDDs have spinning magnetic disks called platters that have been used for computer storage for decades. Here are some defining HDD features:
- Slower speeds – The moving platters cause more latency when accessing data compared to SSDs. This leads to longer load times.
- Moving parts – The mechanical nature of HDDs means they can suffer damage from drops, shocks, vibrations, etc. Making them less durable for mobile use.
- Noisier operation – The physical spinning of platters inside HDDs generates audible noise during use.
- Higher power draw – More electricity needed to spin the platters reduces battery runtime on laptops.
But HDDs have the benefit of being cheaper per gigabyte than similarly sized SSDs. And capacities for HDDs go much higher than SSDs currently.
What’s the difference between an HDD and an SSD?
Here’s a concise summary highlighting the key differences between HDDs and SSDs:
HDDs (hard disk drives) are traditional storage devices that use spinning platters and a mechanical arm to read/write data. This makes them slower and less durable, but cheaper per gigabyte.
SSDs (solid state drives), on the other hand, have no moving parts – data is stored on flash memory chips. This makes SSDs much faster, more shock-resistant, and power efficient. However, they currently offer less storage capacity and higher cost per gigabyte.
In summary:
- Speed: SSDs are significantly faster due to not relying on physical movement to access data
- Durability: No moving parts make SSDs more shock/drop-resistant
- Power: SSDs consume much less electricity resulting in longer laptop battery life
- Capacity: HDDs are available in larger sizes for less cost per GB
- Price: SSDs have a higher cost per gigabyte of storage compared to HDDs
So while HDDs still win on price and maximum capacity, SSD performance, longevity and power savings make them ideal for typical consumer laptop and desktop use cases needing speed along with ample storage.
HDD Pros:
- Far higher maximum capacities
- Cheapest cost per gigabyte
HDD Cons:
- Slower speed by a significant margin
- More vulnerable to physical damage
- Produces noise and heat
- Higher electricity demands
- Generally less reliable long-term
SSD vs HDD: Pros and Cons
Weighing all the comparisons between SSD and HDD technology discussed above, here is a summary of the main advantages and disadvantages when choosing computer storage:
| SSD | HDD |
|---|---|
| Faster speeds (2X to 10X) | Slower speed by a significant margin |
| More durable and shock-resistant | More vulnerable to physical damage |
| Cool, quiet operation | Produces noise and more heat |
| Lower power consumption | Higher electricity demands |
| Typically more reliable | Generally less reliable long term |
| Higher costs compared to HDDs | Cheaper per gigabyte than similarly sized SSDs |
| Primary storage for live system OS/programs and game | Best for storing images, documents and movies |
You see the more detailed difference between SSD and HDD in points below the article.
- Speed Difference Between SSD vs HDD
- SSD vs HDD Storage Capacity
- Power consumption and efficiency
- SSD vs HDD Lifespan
- Is SSD more reliable than HDD?
Speed Difference Between SSD and HDD
When it comes to speed and data transfer rate performance:
- SSDs are significantly faster for most everyday tasks
- HDDs provide slower access times due to physical limitations
Comparing the maximum speeds:
- Top-tier SATA SSDs can reach around 550 MB/s
- High-performance NVMe SSDs boast speeds over 3500 MB/s
- The fastest HDDs max out around 210 MB/s
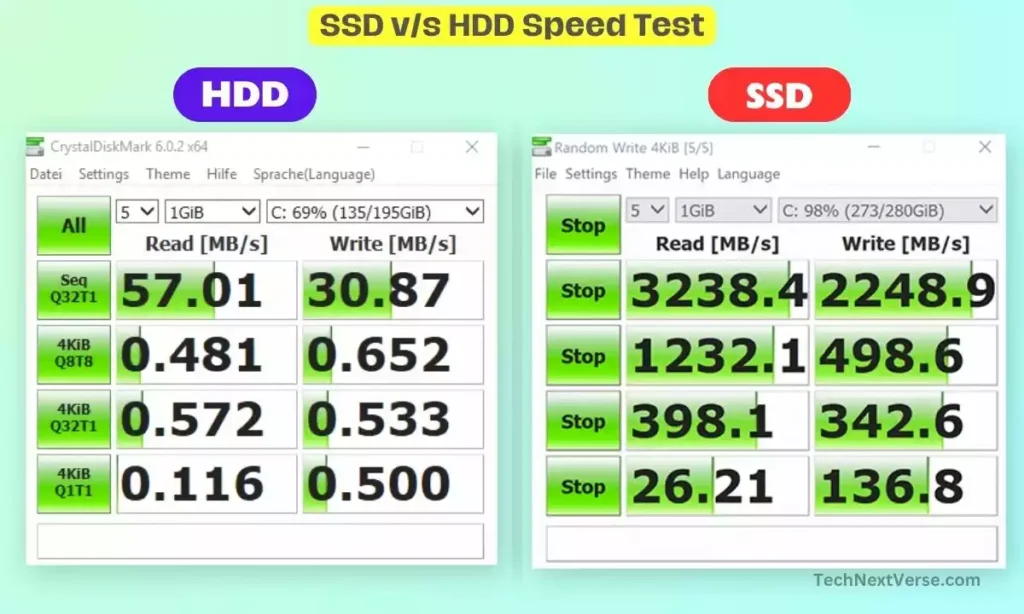
Real-world speeds vary below these peaks. But SSDs will consistently load programs, files, games, and more anywhere from 2 to over 10 times faster than HDDs in the same computer system.
SSD vs HDD Storage Capacity
Storage capacity is a key area where hard disk drives still maintain an advantage over solid-state drives in 2023.
Common capacity tiers for SSDs range from 250GB to 4TB in typical consumer models, though expensive specialized SSDs reach as high as 100TB. Cost per gigabyte remains relatively high for SSDs.
HDD capacities start around 500GB for entry-level options but scale upwards to 10, 14, or even 16 TB per drive in higher-end enterprise models. This provides far more storage density at a lower cost than similarly sized SSDs.
However, SSD technology continues improving – so maximum capacities keep increasing yearly. But currently, HDDs still win for pure storage volume capabilities in many situations.
Power consumption and efficiency
Comparing power draw during operation, SSDs again have a noticeable advantage using much less electricity than HDD systems.
Example idle and load power consumption:
- SATA SSD – 0.2 to 4 watts (light use to heavy load)
- NVMe SSD – 2 to 8 watts range
- HDD – 4 to 12+ watts (fluctuates based on disk activity)
The more consistent power draw of SSDs contributes to improved laptop battery durations along with cooler and quieter operation. Systems stay speedy even when running on battery rather than wall power.
For desktop PCs, electricity costs make minimal impact either way. But every bit of power savings still helps save money and benefit the environment in the long run.
SSD vs HDD Lifespan
All storage devices have a limited useful lifespan before storage degradation and failure. But SSDs and HDDs differ quite a bit in expected longevity.
Typical SSD lifespans range from 5 to 10 years under moderate everyday usage. Current flash memory cells used in quality SSDs have ratings to withstand hundreds to thousands of data write/erase cycles before wear prevents further use.
Whereas HDDs have moving parts that slowly degrade mechanically over longer periods – usually in the 3 to 5-year timeframe under constant use. With careful maintenance, HDDs can sometimes operate successfully for 10+ years.
So while HDDs potentially outlive SSDs in total longevity, the performance and speed of aged HDDs drop considerably over shorter timeframes. In contrast, SSD performance stays consistent nearly up to complete failure.
Is SSD more reliable than HDD?

Yes, SSDs are generally more reliable and durable than HDDs for a few key reasons:
- No moving parts – The solid-state flash memory of SSDs has no mechanical components, unlike the spinning platters and moving heads of traditional HDDs. This makes them far less prone to physical failure.
- Shock/vibration resistance – Without sensitive internal moving parts, SSDs can withstand significantly more shocks, drops, vibrations etc. compared to HDDs.
- Temperature tolerance – SSDs operate fine across a wide temperature range and don’t heat up as much as spinning HDD internals, making them more stable.
- Faster access times – The very fast data access of SSDs results in less accumulated drive stress over time versus HDDs having to physically seek data.
- Read/write endurance – Modern SSDs can withstand hundreds of terabytes being written over their lifespan. Enough for years of intensive operations.
- Encryption – Built-in encryption for data at rest is native to most SSDs protecting the contents if a drive gets lost or stolen.
For heavy-duty applications needing storage reliability over 5+ years, HDDs may still be used.
But for typical mainstream laptop and desktop usage, SSDs are generally a more dependable choice overall. Their lack of moving parts gives SSDs a clear advantage in withstanding the rigours of daily transportation and use.
Is SSD or HDD better for long term storage?
For pure long-term storage needs like archiving data or backups for 5-10+ years, HDDs tend to outlast SSDs in the expected lifespan as mentioned earlier. HDDs also provide much higher capacities for mass storage.
But SSDs have key advantages like speed, stability to magnets/drops/shocks, cooler and quieter operation, as well as lower electricity costs over time. An external SSD keeps data readily accessible for faster recall when needed – while stored away safely in cases of failure of a main computer system.
So consider blending the strengths of each type of storage when planning long-term storage solutions:
- Use SSD as primary storage for live system OS/programs
- Mirror critical data/backups to larger external HDDs
- Store lesser-used files on high-capacity HDDs
- Keep a portable external SSD copy of essential data for grab-and-go convenience
SSD vs HDD: Which is best for Laptop?
For laptop usage, SSDs tend to be the better choice over HDDs for a few key reasons:
- Increased Speed
The fast data access of SSDs means much quicker startup when powering on a laptop and loading programs/files. Everything runs more snappily with an SSD.
- Improved Durability
With no moving parts, SSDs can better withstand being jostled or dropped which happens more often with laptops than desktop computers.
- Longer Battery Life
The lower energy requirements of SSDs result in extended run times on a single laptop battery charge compared to HDD systems.
- Cooler Operation
SSDs give off much less heat than HDDs which reduces cooling needs and fan noise in compact laptop cases.
For these reasons, even lower-capacity SSDs can provide a better overall user experience than larger HDDs in laptop devices.
SSD vs HDD: Which is Better for Gaming?

Gamers stand to benefit tremendously from utilizing solid-state drives to store and run video games rather than traditional hard disk drives.
Games have grown significantly in size, graphics quality, and detail-rich open-world environments in recent years.
So, fast data streaming is crucial for good gameplay experiences. SSDs can directly load textures, levels, and other game assets much quicker than HDDs to travel across expansive game worlds without stutters.
Top 5 reasons SSDs enhance gaming over HDDs:
- Faster Level Loading – Less waiting at splash screens to jump into levels or after death/reload instances
- Smoother Texture Streaming – Details appear faster when rotating the camera in detailed game environments
- Quicker Save & Resume – Easy to save progress more often and get back into game action rapidly from where you left off
- Snappier Response Times – Improves precision of controls and timing actions/reactions during fast-paced play
- Better Multiplayer Sync – Assets streaming speed equals more consistent performance which is vital in online multiplayer matches
While HDDs work fine for simpler or older games – modern triple-A game titles come alive speed-wise on high-performance SSD hardware.
Once gamers try SSDs over HDDs, they won’t want to go back!
What are the disadvantages of SSD over HDD?
Here are some of the main disadvantages SSDs currently have compared to HDDs:
- Higher cost per storage capacity – SSDs remain more expensive per gigabyte than hard drives. Making HDDs better value for very high-capacity bulk storage needs.
- Lower maximum capacities – The highest capacity SSDs reach around 100TB, while HDDs go up to 16TB+ for now. Limiting SSD feasibly for certain server-scale storage projects.
- Lack of TRIM support – Some older operating systems have spotty support for the TRIM command essential to sustaining an SSD’s performance over time. Requiring extra configuration work in some upgrade cases.
- Shorter lifespan with sustained intensive use – While most consumer workloads pose no issue, under very heavy mixed read/write server usage an HDD would outlast an SSD. However, the SSD would be much faster during its usable duration.
- File recovery challenges – Retrieving erased files from flash cells can be difficult for SSDs, whereas HDD recovery tools have higher success from magnetic platters.
However, for general home and office use SSD advantages like speed, power efficiency, shock resistance, encryption capabilities, form factor, etc.
HDD downsides like slower access, spin-up delays, larger form factors tend to have a more noticeable everyday impact. So SSDs now make sense as the default choice for average computer applications.
what are the main differences between HDD and SSD?
Here’s a brief summary of the main differences between hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid state drives (SSDs):
HDDs:
- Store data on spinning magnetic platters
- Slower read/write speeds
- Vulnerable to physical shock
- Noisier operation
- Cheaper per GB of storage
- Higher capacities available
SSDs:
- Store data on flash memory chips
- Much faster access speeds
- More durable and shock-resistant
- Silent operation
- Uses less power
- Currently more expensive per GB
- Lower maximum capacities
In short – HDDs are affordable high-capacity storage, while SSDs are faster, more reliable drives. SSDs excel at speed for active use cases, HDDs offer dense bulk storage. Using both can provide complementary strengths.
FAQs
Is SSD is better than HDD?
Yes, SSDs are faster, more reliable, and more power efficient due to their flash memory-based solid-state design lacking moving parts. This makes them ideal for typical client devices like laptops.
Which is better for storage SSD or HDD?
When it comes to storage, SSDs are generally better for active speed-sensitive use cases, while HDDs are better for cost-effective archival bulk storage.
Is it better to upgrade RAM or SSD?
Upgrading to an SSD will provide more noticeable general performance improvements over upgrading RAM for most average users.
Is SSD or HDD better for gaming?
For gaming purposes, SSDs provide a substantially better experience overall compared to traditional HDDs.
SSDs massively decrease load times for game levels, textures, transitions, and saves. This reduces friction and dead time waiting on seeks.
The instant data access of SSDs enables much smoother streaming of rich open game worlds without hitches.
Conclusion
Hopefully, this guide gave you a helpful high-level understanding of the difference between HDD and SSD storage drives for computers!
Also, you know what is the advantage of using SSD rather than HDD.
As a tech friend, I suggest you buy a 500GB SSD and install the fresh Windows 10 or 11, and watch the magic happen!
If you have any questions you can ask me in the comment section.








